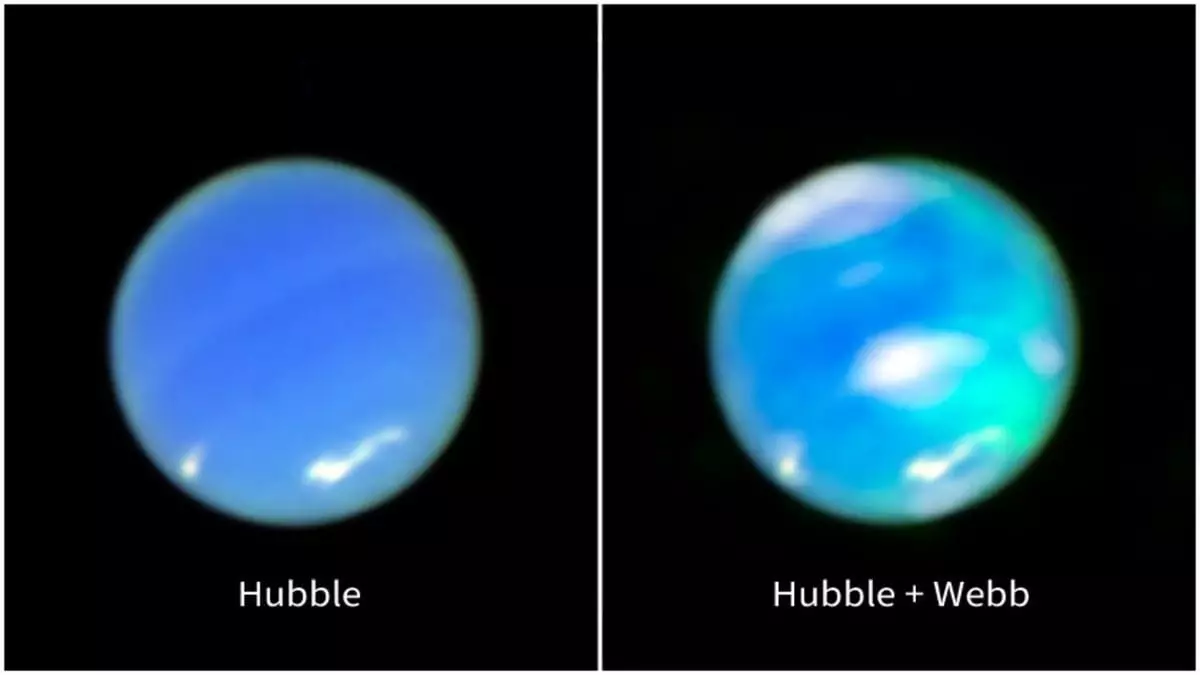
In an awe-inspiring leap for planetary science, Neptune’s elusive auroras have finally been unveiled, with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) pioneering this visual revelation. After a prolonged period of speculation and educated guesses, researchers have been able to capture what was once merely an abstract concept. This astonishing feat underscores not just the advancements in our observational technologies, but also a compelling reminder of how little we truly understand about our cosmic neighbors.
Until now, most of what we knew about Neptune’s atmospheric phenomena was largely drawn from historical data, particularly from the Voyager 2 mission, which offered tantalizing hints but no definitive visuals. The JWST’s capacity for near-infrared observation has now shattered previous limitations, yielding images that bring Neptune’s majestic auroras to life. With the confirmation of these spectacular displays, we enter an era where our quest for knowledge about our solar system reaches new heights.
Auras Beyond Expectations
What sets Neptune’s auroras apart from those of other celestial bodies like Earth or Jupiter is their unpredictable locations. On those planets, auroras are typically concentrated near the polar regions; however, Neptune’s magnetic field—a very tilted and uniquely offset one—has upended these expectations. Charged particles from the solar wind dance in chaotic patterns across the planet, creating auroras in unexpected locales. This revelation not only highlights Neptune’s individuality among the gas giants but also poses provocative questions about how we understand magnetospheres and atmospheric behavior in planetary science.
Henrik Melin, a prominent planetary scientist, remarked on the sheer unpredictability of these auroras. Seeing them in such detail was not just fortuitous; it was groundbreaking. The challenge of visualizing these celestial phenomena goes to showcase the limitations of earlier exploratory missions, where expectations often fell short of cosmic realities. It emphasizes the extraordinary capabilities of modern telescopes, which have redefined our capacity to explore and appreciate the universe surrounding us.
Temperature Shifts and Implications for Future Studies
Intriguingly, the JWST’s observations also revealed that Neptune’s upper atmosphere is cooling significantly, dropping to temperatures just over half of what was recorded during Voyager 2’s flyby in 1989. This chilling discovery adds layers of complexity to the dynamics of Neptune’s atmospheric conditions, suggesting that the weakening auroras could be a direct result of these temperature declines. As researchers grapple with these findings, it raises pressing concerns about future missions to outer planets. Will our current tools be sufficient to unravel the mysteries these environments hold, or do we need further advancements?
Heidi Hammel, a leading JWST scientist, emphasized that the presence of the trihydrogen cation (H₃⁺) signifies ongoing auroral activity and asserts that what we see on Neptune corresponds with observations made on other gas giants. This leap in understanding is instrumental for the scientific community, indicating not only that we are beginning to unveil Neptune’s secrets, but that further exploration and refinement in our observational approach are more necessary than ever before.
By shedding light on Neptune’s spectral wonders, we enter an exhilarating chapter in planetary science—one teeming with promising opportunities and new inquiries about the vastness of our universe.